L Walser-Reinhard, D Schaarschmidt-Kiener, J L Forster, F Matheis, B Spiess
DOI: 10.1024/0036-7281/a000318
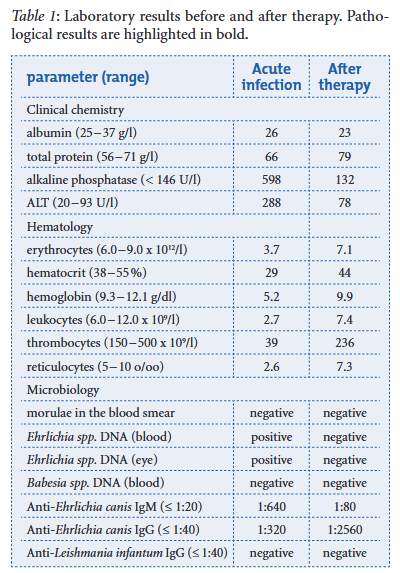
A one-year-old Maltese dog imported from Brazil was presented because of anorexia, dehydration, fever and palpable mandibular lymph nodes. The dog developed clinical signs of bilateral blepharospasm, photophobia and anterior uveitis a few days later. Monocytic ehrlichiosis was diagnosed by positive PCR results from both EDTA blood and conjunctival samples. In addition, Ehrlichia canis-specific IgM and IgG antibodies were both detected. One week after starting treatment with systemic doxycycline and local anti-inflammatory and cycloplegic therapy the dog recovered from systemic and eye diseases. After therapy the follow-up examination revealed a full remission of clinical and hematological parameters and a negative PCR result.